# Middlewares
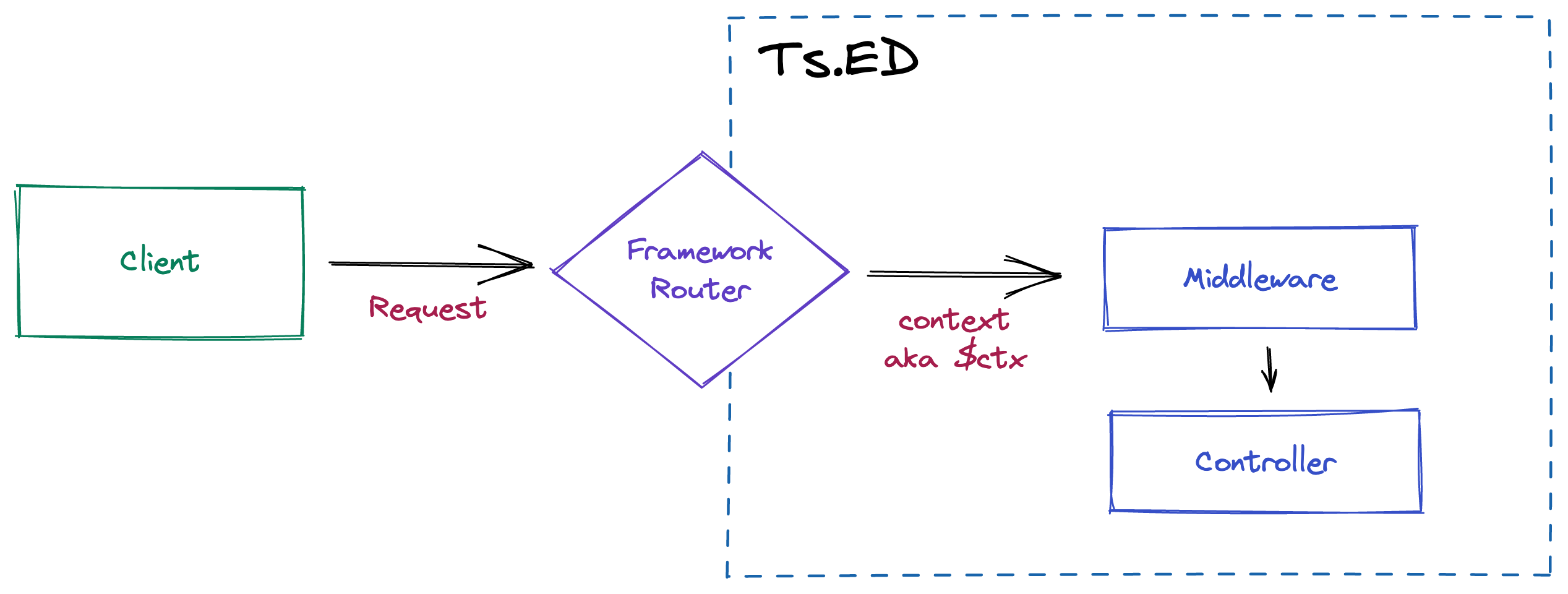
Middleware is similar to the Express middleware with the difference that it's a class and you can use the IoC to inject other services on its constructor.
All middlewares decorated by
Middleware
have one method named use().
This method can use all parameters decorators as you can see with the Controllers and return a promise.
# Configuration
To begin, you must add the middlewares folder to the componentsScan attribute in your server settings as follows:
import {Configuration} from "@tsed/di";
import {MyController} from "./controllers/rest/MyController";
@Configuration({
mount: {
"/rest": [MyController]
}
})
export class Server {}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
Then, create a new file in your middlewares folder. Create a new Class definition and then add the Middleware decorator.
import {Context} from "@tsed/platform-params";
import {Middleware} from "@tsed/platform-middlewares";
@Middleware()
export class CustomMiddleware {
use(@Context() $ctx: Context) {
console.log("ID", $ctx.id);
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
There are different use cases for declaring and using middleware, as follows:
- Global middleware: this middleware can be used on the Server,
- Endpoint middleware: this middleware can be used on a controller method,
- Error middleware: this middleware can be used to handle errors.
Note
Global middleware and endpoint middleware are similar, except that the Endpoint middleware can access the last executed endpoint information.
# Global middleware
Global middlewares are generally used to handle requests before or after controllers.
import {Context} from "@tsed/platform-params";
import {Constant} from "@tsed/di";
import {MiddlewareMethods, Middleware} from "@tsed/platform-middlewares";
import {NotAcceptable} from "@tsed/exceptions";
@Middleware()
export default class AcceptMimesMiddleware implements MiddlewareMethods {
@Constant("acceptMimes")
acceptMimes: string[];
use(@Context() $ctx: Context) {
if (!$ctx.request.accepts(this.acceptMimes)) {
throw new NotAcceptable("Accepted mimes are: " + this.acceptMimes.join(", "));
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
Then add your middleware to the Server by using the right hook:
import {PlatformApplication} from "@tsed/common";
import {Configuration, Inject} from "@tsed/di";
import {GlobalAcceptMimeMiddleware} from "./GlobalAcceptMimeMiddleware";
@Configuration({
acceptMimes: ["application/json"] // add your custom configuration here
})
export class Server {
@Inject()
app: PlatformApplication;
$beforeRoutesInit() {
this.app.use(GlobalAcceptMimeMiddleware);
}
// or
$afterRoutesInit() {
this.app.use(GlobalAcceptMimeMiddleware); // But maybe is too late ;)
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
It's also possible to register middlewares using middlewares option in the
Configuration
decorator.
In addition, it's also possible to configure the environment for which the middleware should be loaded.
import {Configuration, ProviderScope, ProviderType} from "@tsed/di";
@Configuration({
middlewares: [
{hook: "$afterInit", use: helmet({contentSecurityPolicy: false})},
{env: Env.PROD, use: EnsureHttpsMiddleware},
cors(),
cookieParser(),
compress({}),
methodOverride(),
AuthTokenMiddleware
]
})
export class Server {}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
The middlewares added through middlewares option will always be registered after the middlewares registered through the hook methods!
::: warn
Only Express/Koa middlewares can be added to $beforeInit, $onInit and $afterInit hooks. At this step the PlatformContext is not available. Injectable Ts.ED middleware won't work as expected.
To add Ts.ED middleware, use the $beforeRoutesInit hook (it's the default hook value) or leave the hook property empty.
:::
# Endpoint middleware
Endpoint middleware is not really different from global middleware, but its goal is to handle a request before or after an endpoint. It knows which endpoint is executed by using the EndpointInfo decorator.
The following example shows you how to implement the middleware and use it with a custom decorator.
Middleware can be used on a class controller or an endpoint method with the following decorators:
import {UseBefore} from "@tsed/platform-middlewares";
import {Get} from "@tsed/schema";
import {Controller} from "@tsed/di";
import {CustomMiddleware} from "./middlewares/CustomMiddleware";
@Controller("/test")
@UseBefore(CustomMiddleware) // global to the controller
class MyCtrl {
@Get("/")
@UseBefore(CustomMiddleware) // only to this endpoint
getContent() {}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
TIP
If your middleware isn't correctly placed in the call sequence, you can use the priority property to change the order.
@Middleware({
priority: -1
})
class MyMiddleware {}
2
3
4
Note: This option is only available for middlewares added to a controller or endpoint method.
# Error middleware
Express allows you to handle any error when your middleware has 4 parameters like this:
function (error, req, res, next){}
Ts.ED has the same mechanism with the Err decorator. Use this decorator on a middleware to create a handler which will only be called when an error occurs on the decorated endpoint.
import {Err, Middleware, Next} from "@tsed/common";
@Middleware()
export class MyMiddlewareError {
use(@Err() err: unknown, @Next() next: Next) {
console.log("===> Error:", err);
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
The following example is the GlobalErrorHandlerMiddleware used by Ts.ED to handle all errors thrown by your application.
If you plan to catch errors globally see our Exception filter page.
# Specifics parameters decorators
In addition, you have these specific parameters decorators for the middlewares:
| Signature | Description |
|---|---|
| Err | Inject the Express.Err service. |
| Context | Provide all information about the called endpoint |
# Call sequences
As you saw in the previous section, a middleware can be used in different contexts:
A middleware added to a controller or endpoint level has the same constraint as the endpoint method itself. It will be executed only when the url request matches with the path associated with the controller and its endpoint method.
When a request is sent to the server all middlewares added at the Server, Controller or Endpoint level with decorators will be called until one of the handlers/middlewares in the stack sends a response.

For each executed endpoints and middlewares, Platform API stores the return value in the Context . We have two scenarios:
- If data is stored in the Context object, the response will be immediately sent to your consumer after the UseAfterEach middleware (if present).
- If no data is stored in the Context object, the call sequence middlewares continue to the next endpoint (if present) or to the UseAfter then Global middlewares until data is returned by a handler.
TIP
The middlewares shown in the Endpoints box will be executed as many times as there are endpoints that match the request url.
For example:
import {Next} from "@tsed/common";
import {Use, UseAfter, UseBefore, UseBeforeEach} from "@tsed/platform-middlewares";
import {Get} from "@tsed/schema";
import {Controller} from "@tsed/di";
@Controller("/")
@UseAfter(MdlwCtrlAfter)
@UseBefore(MdlwCtrlBefore)
@UseBeforeEach(MdlwCtrlBeforeEach)
@Use(MdlwCtrl)
export class MyCtrl {
@Get("/")
@UseBefore(MdlwBefore)
@Use(Mdlw)
@UseAfter(MdlwAfter)
endpointA(@Next() next: Next) {
console.log("EndpointA");
next();
}
@Get("/")
endpointB() {
console.log("EndpointB");
return {};
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
According to the call sequence scheme, the stack calls will be as follows:
- Middlewares added to the Server (logger, express middleware, etc...),
- MdlwCtrlBefore,
- MdlwCtrlBeforeEach
- MdlwBefore,
- MdlwCtrl,
- MyCtrl.endpointA,
- MdlwAfter,
- SendResponse, (but no data is returned by the endpointA)
- MdlwCtrlBeforeEach
- MdlwCtrl,
- MyCtrl.endpointB,
- MdlwAfter,
- SendResponse, sends a response because endpointB returns data,
- MdlwCtrlAfter, but this middleware will not be called because a response was sent.
- Middleware added to the Server (not called too).
# Override existing middlewares
The decorator OverrideProvider gives you the ability to override some internal Ts.ED middlewares.
import {OriginalMiddleware} from "@tsed/common";
import {Context} from "@tsed/platform-params";
import {OverrideProvider} from "@tsed/di";
@OverrideProvider(OriginalMiddleware)
export class CustomMiddleware extends OriginalMiddleware {
public use(@Context() $ctx: Context) {
$ctx.response; // Ts.ED response
$ctx.request; // Ts.ED resquest
$ctx.getResponse(); // return Express.js or Koa.js response
$ctx.getRequest(); // return Express.js or Koa.js request
// Do something
return super.use();
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
Here we use the new Platform API to write our middleware. By using the Context decorator and PlatformContext class we can get some information:
- The data returned by the last executed endpoint,
- The EndpointMetadata itself,
- The PlatformRequest and PlatformResponse classes abstraction. These classes allow better code abstraction by exposing methods that are agnostic of Express.js.
TIP
By default, the server imports automatically your middlewares that match with these rules ${rootDir}/middlewares/**/*.ts (See componentScan configuration).
.
├── src
│ ├── controllers
│ ├── services
│ ├── middlewares
│ └── Server.ts
└── package.json
2
3
4
5
6
7
If not, just import your middleware into your server or edit the componentScan configuration.
import {Configuration} from "@tsed/common";
import "./src/other/directory/CustomMiddleware";
@Configuration({
...
})
export class Server {
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
# Provided middlewares
Last Updated: 10/24/2024, 6:33:40 AM
Other topics
- Session & cookies
- Passport.js
- Keycloak
- Prisma
- TypeORM
- MikroORM
- Mongoose
- GraphQL
- GraphQL WS
- Apollo
- TypeGraphQL
- GraphQL Nexus
- Socket.io
- Swagger
- AJV
- Multer
- Serve static files
- Templating
- Serverless HTTP
- Seq
- OIDC
- Stripe
- Agenda
- Terminus
- Serverless
- Server-sent events
- IORedis
- Vike
- Jest
- Vitest
- Controllers
- Providers
- Model
- JsonMapper
- Middlewares
- Pipes
- Interceptors
- Authentication
- Hooks
- Exceptions
- Throw HTTP Exceptions
- Cache
- Command
- Response Filter
- Injection scopes
- Custom providers
- Lazy-loading provider
- Custom endpoint decorator
- Testing
- Customize 404